Art, in its many forms, has been a cornerstone of human culture for millennia. From the cave paintings of our ancestors to the digital art of today, it has always been a medium for expression, communication, and reflection. However, the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has brought about a seismic shift in the art world, particularly in the realms of realism and photorealism. While AI has the potential to revolutionize these art movements, it also poses significant challenges and threats.
## The Rise of AI in Art
AI's involvement in art is not a new phenomenon. In fact, it has been gradually infiltrating the art world for several years now. AI algorithms can now generate artwork, and some of these pieces have even been sold at prestigious auction houses.
(images created at random using Midjourney)
However, the impact of AI on art is not limited to the creation of new pieces. It also extends to the way we interact with and interpret art. For instance, AI can analyze artwork and provide insights into the artist's style, technique, and influences, enhancing our understanding and appreciation of the piece.
## The Negative Impact of AI on Realism and Photorealism
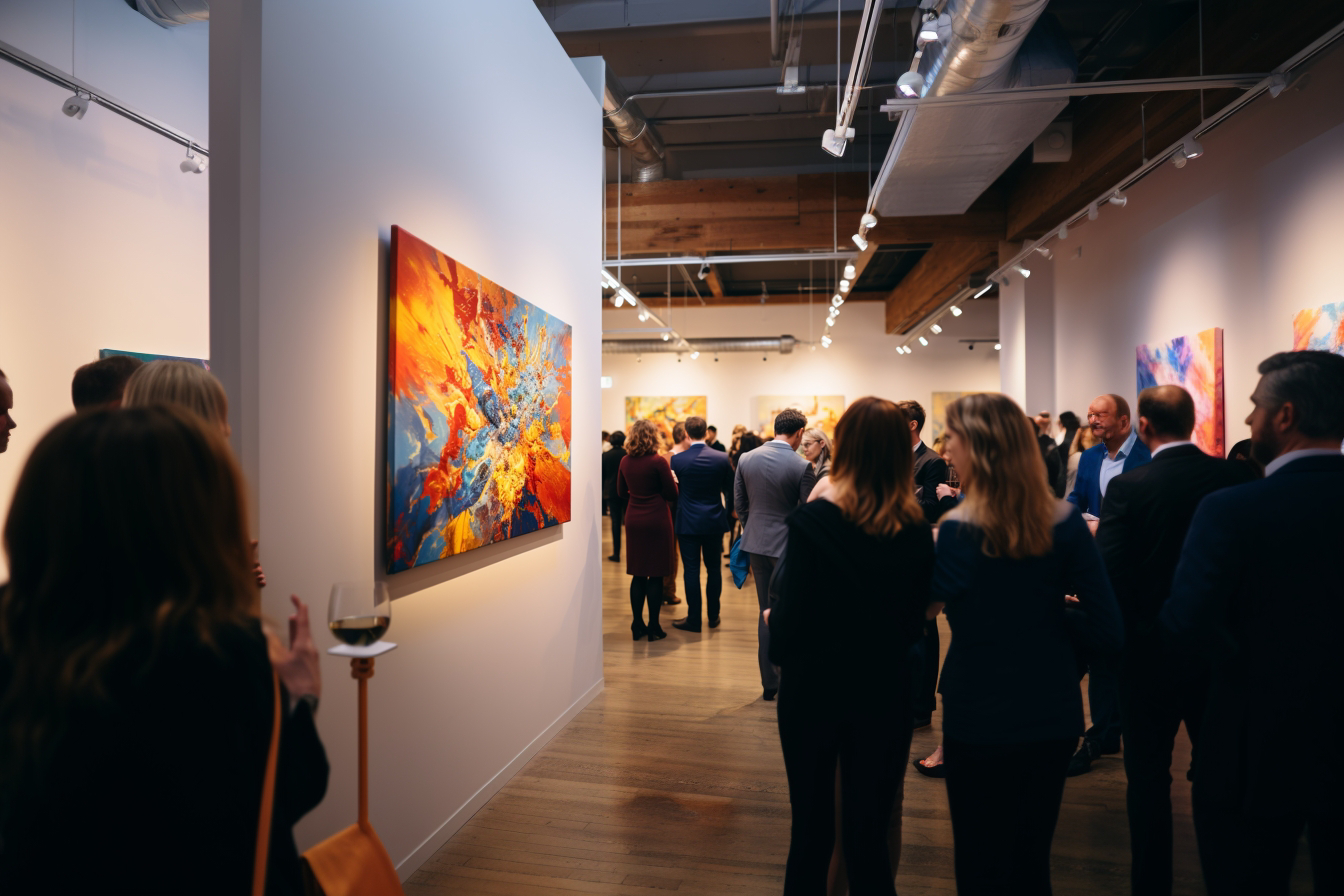
Realism and photorealism are art movements that strive to depict their subjects with a high level of detail and accuracy, often to the point where the artwork can be mistaken for a photograph. These movements require a significant amount of skill, patience, and attention to detail from the artist.
(Spanish hyperrealist, Pedro Campos and his paintings are the apex of hyperrealistic paintings today. Images: Plus One Gallery, London)
However, the rise of AI has posed a significant threat to these art movements. Here's why:
### 1. Devaluation of Skill
One of the main challenges is that AI can replicate the detailed and precise style of realism and photorealism with relative ease. This has the potential to devalue the skill and effort that artists put into their work. After all, why spend hours painstakingly creating a realistic painting when an AI can produce a similar piece in a fraction of the time?
### 2. Loss of Uniqueness
Art is often valued for its uniqueness and the personal touch of the artist. However, although AI-generated art lacks this personal touch, it can replicate the style and artworks of artists that have been included in its learning model, and it can easily replicate them, which could lead to a loss of uniqueness in the art world.
### 3. Ethical Concerns
There are also ethical concerns associated with AI-generated art. For instance, who owns the copyright to an AI-generated piece? Is it the creator of the AI, the user who generated the artwork, or the AI itself? These questions are yet to be definitively answered, creating a murky ethical landscape.
## The Potential of AI in Enhancing Realistic Artwork
Despite these challenges, AI also offers several opportunities to enhance realism and photorealism.
### 1. Assisting Artists
AI can be used as a tool to assist artists, rather than replace them. For instance, AI can help artists with the more tedious aspects of creating realistic art, such as getting the proportions and perspective right, allowing them to focus more on the creative aspects of their work.
### 2. Expanding Creative Possibilities
AI can also expand the creative possibilities for artists. For instance, AI algorithms can generate new and unique patterns, shapes, and colors, which artists can incorporate into their work.
AI could even aid in the conceptual aspects of art creation that humans have not conceived of before now. Beyond the creative stages of the artwork, AI can also help in the marketing and branding business side of the artist's career - the part which few artists enjoy.
### 3. Enhancing Accessibility
AI can make the creation of realistic art more accessible. Not everyone has the time, resources, or skill to create realistic art, but with AI, anyone can create a realistic piece of art with a few clicks of a button.
## The Future of Photorealistic Art in Conjunction with AI
Looking to the future, the integration of AI in the art world is likely to continue, and its influence on realism and photorealism will evolve. Here are a few possibilities:
### 1. Hybrid Art
We may see the rise of hybrid art, where artists and AI collaborate to create pieces that combine the best of both worlds: the creativity and personal touch of the artist, and the precision and efficiency of AI-generated systems.
### 2. New Art Movements
The integration of AI in art could also give rise to new art movements that blend traditional techniques with AI-generated elements. This could lead to a whole new era of creativity and innovation in the art world.
### 3. Enhanced Art Education
AI could also revolutionize art education. For instance, AI could be used to create interactive tutorials that adapt to the learner's skill level, making it easier for people to learn and master the techniques of realism and photorealism.
In conclusion, while AI poses significant challenges to the art world, particularly in the realms of realism and photorealism, it also offers exciting opportunities for enhancement and innovation. As with any technological advancement, it is up to us to navigate these challenges and harness the potential of AI to enrich, rather than diminish, our artistic endeavors.